What is Virtualized Storage?
Virtualized storage, or storage virtualization, is a technological concept developed within the past few decades. It enables organizations to remove the traditional boundaries of physical storage devices, by abstracting the disks and drives, and presenting them as a single, centralized pool of storage capacity. Storage virtualization software identifies the amount of storage capacity available across the physical storage components, compiles it, and provides it to the applications for use.
How Does Storage Virtualization Work?
Historically, each individual application being used by a business required its own dedicated hardware – think print servers, email servers, etc. As organizations began utilizing more and more applications to simplify day-to-day operations, their datacenters became complex, costly, and overcrowded, to accommodate all of their physical hardware.
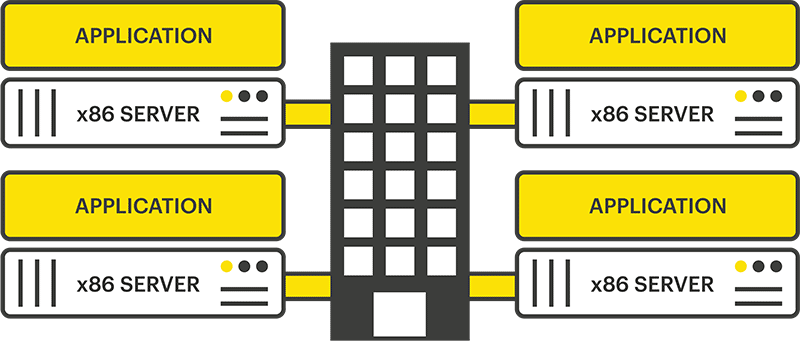
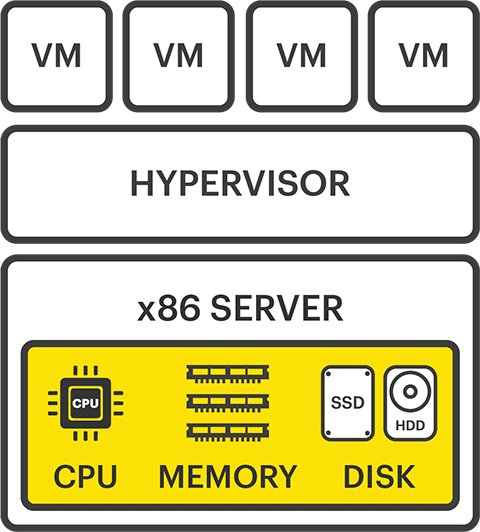
To address these challenges, IBM created the concept of “virtualization,” in the mainframe world, and VMware figured out how to bring mainframe virtualization into the x86 server space. Instead of only being able to run a single application per server, VMware discovered how to virtualize the hardware (memory, CPU, and disk), so multiple operating systems could run at the same time. They created a layer called a hypervisor, which divides up those physical resources, virtualizes them, and carves off a piece for each guest operating system (i.e. virtual machine – VM).
The hypervisor concept enabled organizations to use more affordable and common x86 servers to run multiple applications at once on a single piece of hardware. What it didn’t provide was a way to share storage resources, and the applications themselves across multiple servers – applications were ‘siloed’ within their hardware and if the server failed, the data and applications would go offline. Therefore to prevent such downtime events, hypervisors developed features such as VMware’s vMotion and Fault Tolerance. These features allow data and applications to be migrated from one server to another but require a shared storage network to operate.
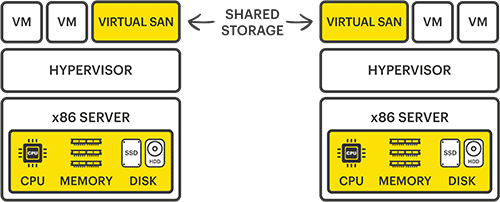
Shared storage introduced the concept of high availability to help reduce the likelihood of downtime events impacting business productivity and revenue. To achieve high availability and leverage the advanced hypervisor features introduced by the likes of VMware, specialist storage hardware such as physical SANs and NAS devices were utilized. Over time, these dedicated components have also been virtualized and incorporated into the same x86 servers running the hypervisor. This virtualization concept is known as a virtual SAN
What Are the Benefits of Storage Virtualization?
Making the switch from legacy data storage infrastructure to virtualized storage architecture delivers several benefits to organizations. These include:
Simplicity:
One of the main advantages of transitioning from traditional data storage infrastructure to a virtualized storage model, is the ability to massively simplify your IT environment. Making the switch to storage virtualization eliminates complexities in the datacenter, by reducing the amount of hardware needed to run applications. Traditional data storage models require separate servers for individual applications, whereas storage virtualization enables those same applications to be run from one or a greatly reduced number of servers.
Affordable:
Cost is another key benefit of storage virtualization. The traditional datacenter required many more servers and therefore a far more complex infrastructure and network, greatly increasing upfront expense and also costs to maintain over time. Storage virtualization reduces both CAPEX and OPEX costs, requiring far less resources (i.e. hardware, physical space, operating expenses, IT support). It is lightweight, and essentially requires less of everything, making it significantly more affordable.
Modernization:
The old methodologies of traditional siloed applications and data storage have been well and truly left behind. Transitioning to storage virtualization opens up huge new opportunities for organizations to take advantage of the latest developments in virtualization, software-defined technologies and hyperconvergence.
Storage Virtualization and Edge Computing
An edge computing environment can be classified as any IT site located outside the datacenter or cloud. Examples of edge sites include retail stores, manufacturing sites, travel and tourism organizations, remote and branch offices, and industrial IoT. These environments often face several unique challenges, such as limited onsite IT support, finite physical space, and restricted budgets (as they often have many sites to manage).
Storage virtualization isn’t just an option for edge computing environments, it’s a necessity. Edge organizations are commonly located in remote places, and often have tens, hundreds, or even thousands of sites to maintain, and traditional datacenter architecture just isn’t feasible for them. They need lightweight, simple IT that can be managed centrally, and doesn’t require constant maintenance.
A retail store or remote office doesn’t always have a designated IT specialist on site to help facilitate updates or repairs as needed. Virtualizing their storage at the edge gives an organization an infrastructure that is much more simple to manage. It is also more compact, making it ideal for organizations with limited space, as well as more affordable, requiring less hardware and resources.
Check out our Beginners Guide to Edge Computing for additional information about the unique requirements of edge environments, how edge computing works, and the benefits of edge computing solutions.
Additional Virtualized Storage resources you may find helpful:
SvSAN and Virtualized Storage
StorMagic SvSAN is a virtual SAN, based on software-defined storage, that delivers simple, flexible, and reliable storage to SMBs and edge environments. Using a hypervisor’s storage virtualization, SvSAN turns the underlying storage of any x86 server into highly available shared storage, within clusters of two or three server nodes, or more.
Some of the benefits offered by StorMagic SvSAN include: