What is Edge Computing?
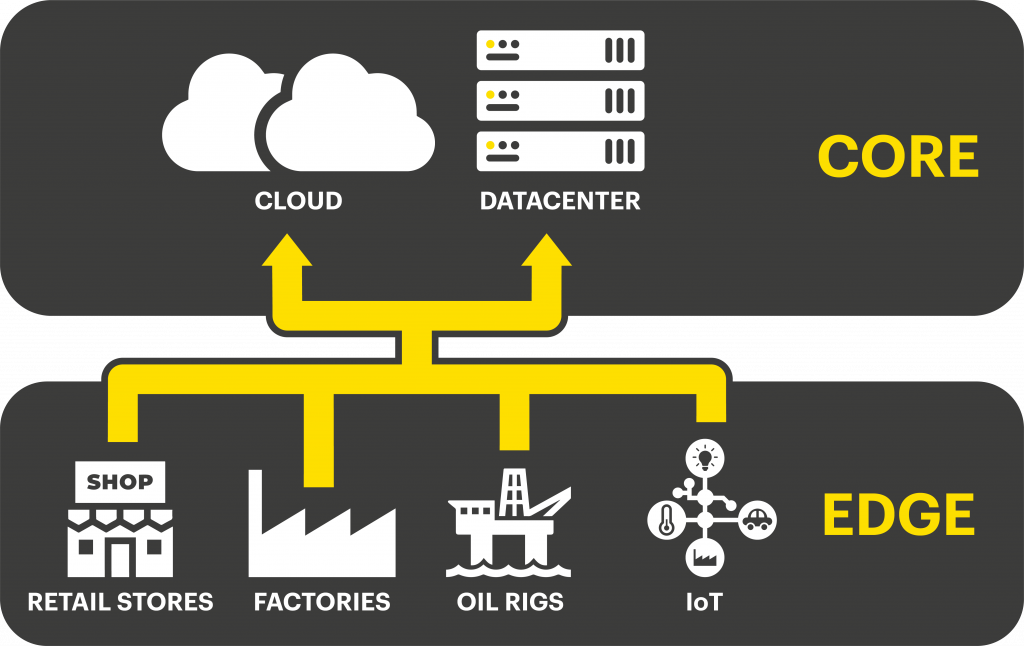
Edge computing is a term used to describe decentralized IT infrastructure. In an edge computing environment, applications, computation, and data storage are all carried out near the source of the data (i.e. at the “network edge”), as opposed to in the cloud or at an offsite datacenter. By processing data locally and minimizing the distance between devices and servers, edge computing delivers improved performance, requires less bandwidth, and reduces latency.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Traditional IT infrastructure requires data to be transmitted across lengthy distances and multiple network connections, which may require substantial bandwidth and hardware. Edge computing brings compute and storage resources closer to where the data is generated, reducing the distance it has to travel. Rather than sending the data off to the cloud, or pushing it to a central datacenter, it allows for real-time processing of applications within close physical proximity to the end user.
Through the use of virtualization technology and software-defined storage, edge computing enables users to deploy and run their applications, while ensuring high availability, through software installed on their edge servers. For compute-intensive environments, organizations can implement a hybrid compute model, where high-demand applications are processed near the source and others are transmitted to a central datacenter location.
What Are the Benefits of Edge Computing?
Many organizations today are creating massive amounts of data, requiring fast transfer rates and response times, which often aren’t feasible when it comes to traditional IT infrastructure. Edge computing solutions offer several user benefits, including:
High Availability
Downtime and slow response times are detrimental to businesses, resulting in decreased productivity, damage to brand reputation, and even loss of revenue. Edge computing can ensure high availability for applications and data, by leveraging a virtualized shared storage solution such as a virtual SAN on the hardware at the edge site. A highly available configuration can eliminate downtime, which keeps vital applications online, productivity high and customers satisfied.
More Affordable
As businesses grow, edge computing solutions enable them to scale more cost-effectively. The hardware required at edge sites costs less – it doesn’t have to be datacenter-class, and the organization often does not need to install costly high capacity networking links for additional bandwidth and mitigate against latency. As well as latency, edge computing also helps mitigate against another common IT problem that can significantly impact revenue: downtime.
Increased Reliability
With traditional datacenter models, data is processed and stored centrally, and an outage at that central location is therefore much more likely to affect the entire organization. Edge computing solutions reduce the threat of such scenarios by decentralizing resources, allowing each site to operate effectively on its own, minimizing the damage of network issues. Distributing applications, processing, and storage makes it more difficult for a single disruption, such as a localized natural disaster, to take down the entire organization.
Several different types of environments benefit from implementing edge computing solutions, including remote and branch offices, retail stores, industrial IoT, and manufacturing sites.
Additional Edge Computing resources you may find helpful:
SvSAN and Edge Computing
StorMagic has been building and delivering solutions for the edge for over a decade. SvSAN was built specifically to address the needs of edge computing environments, providing increased uptime, simplicity, and extreme low cost for edge customers, without sacrificing performance or enterprise-class features.
There are many ways to deploy, use, and scale SvSAN to meet your exact needs. SvSAN has over a dozen enterprise-grade features included with the base license, and you can choose how to implement, what else you need, and how you will grow.