What is Cybersecurity?
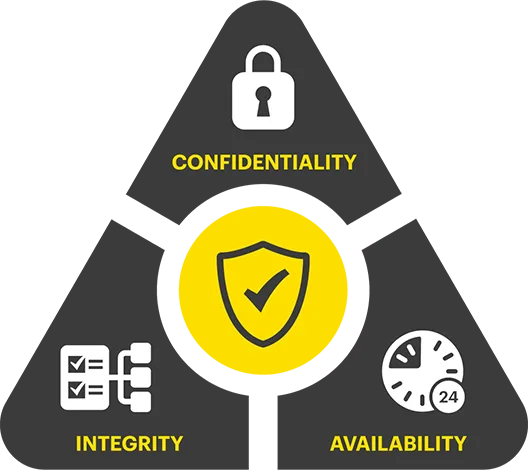
Cybersecurity is a term used to describe the practice of defending networks, devices, applications, and data from unauthorized access, hacking, malware, and other forms of cyber threats. It consists of a variety of different technologies, tools, processes, and approaches, for ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, also known as the CIA triad. They are just a few pieces of a cybersecurity framework that comprises the following aspects:
- Confidentiality: Protecting data from being accessed by unauthorized individuals. This is often achieved through encryption and access controls.
- Integrity: Ensuring that data remains accurate and unaltered by unauthorized parties. This involves mechanisms to detect and prevent data tampering.
- Availability: Ensuring that systems and data are accessible when needed, preventing disruptions or downtime due to cyberattacks or other incidents.
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of users and devices to ensure that only authorized individuals or entities have access to the system.
- Authorization: Determining what actions or resources users or systems are allowed to access based on their roles and permissions.
- Accounting: logging and monitoring information on users’ resource usage.
- Security measures: Implementing various security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and security policies to protect against cyber threats.
- Risk management: Identifying and assessing potential vulnerabilities and threats and developing strategies to mitigate or manage them.
- Incident response: Developing plans and procedures to address and recover from security incidents, such as breaches or cyberattacks.
As the world becomes increasingly dependent on technology, it’s no surprise that cybersecurity has become a hot topic. This holds particularly true for businesses that are producing, storing, and sharing mass amounts of sensitive information all the time. The impact of a breach on a business will almost certainly be detrimental, therefore it’s important that organizations take the necessary precautions to keep their assets secure.
Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted the business world, shifting many employees from working in offices to working remotely from home. This change has transitioned many digital access points and data collection locations from corporate datacenters to mobile devices, home offices, edge computing and cloud computing. It has increased the size of the cyberattack surface, opening up several new avenues for threats to enter through (attack vectors).
How Does Cybersecurity Work?
According to Gartner, worldwide end-user spending on security and risk management is projected to total $215 billion in 2024, an increase of 14.3% from 2023. Organizations do realize the growing importance of cybersecurity, and continue to implement tools and practices to keep their systems, employees, and information secure.
An organization typically has a complex technological architecture, composed of many different pieces and parts (i.e. networks, applications, computers, and IoT devices) which require a commitment to a defense-in-depth approach with multiple, overlapping security controls utilized to achieve CIA triad objectives.
Each of these components requires a combination of cybersecurity solutions to protect it. For example:
Network Security
![]() Firewalls, Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS), Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), Network Access Control (NAC), and SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) are used to protect a network from being infiltrated by unauthorized parties.
Firewalls, Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS), Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), Network Access Control (NAC), and SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) are used to protect a network from being infiltrated by unauthorized parties.
Endpoint Security
![]() This is an approach used to protect laptops, tablets, mobile phones, and other devices from being exploited by malicious actors (e.g. antivirus, threat detection, encryption, and mobile device management (MDM)).
This is an approach used to protect laptops, tablets, mobile phones, and other devices from being exploited by malicious actors (e.g. antivirus, threat detection, encryption, and mobile device management (MDM)).
Application Security
![]() Also known as “AppSec”, this refers to the practice of securing software applications and systems from various security threats, vulnerabilities, and attacks. Key aspects of application security include: identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities, secure software development, data encryption, and compliance.
Also known as “AppSec”, this refers to the practice of securing software applications and systems from various security threats, vulnerabilities, and attacks. Key aspects of application security include: identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities, secure software development, data encryption, and compliance.
Cloud Security
![]() These are software-based tools used to protect and monitor data in the cloud (e.g. cloud-specific security services, encryption, identity and access management (IAM), and cloud access security brokers (CASB)).
These are software-based tools used to protect and monitor data in the cloud (e.g. cloud-specific security services, encryption, identity and access management (IAM), and cloud access security brokers (CASB)).
Effective cybersecurity within an organization relies on the establishment of comprehensive policies and processes to identify, manage, and mitigate security risks. These policies and processes help ensure that security measures are consistently applied, and that employees, systems, and data are protected. Here are some common policies and processes that organizations typically implement for cybersecurity:
- Information Security Policy: This policy outlines an organization’s commitment to protecting sensitive information, including data classification, handling, and retention. It also provides an overview of the organization’s approach to cybersecurity.
- Acceptable Use Policy (AUP): An AUP defines the acceptable use of organizational resources, including computers, networks, and internet access. It specifies what employees can and cannot do with these resources and helps prevent misuse.
- Data Protection and Privacy Policy: This policy addresses how personal and sensitive data are collected, stored, processed, and protected, ensuring compliance with relevant data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Access Control Policy: Access control policies define how users are granted access to systems, data, and applications. They include role-based access, strong authentication requirements, and access revocation processes.
- Password Policy: A password policy outlines the rules for creating and maintaining passwords, including complexity requirements, expiration periods, and how to handle forgotten or compromised passwords.
- Incident Response Plan: This plan outlines the steps to take when a security incident or data breach occurs. It includes roles and responsibilities, communication strategies, and procedures for investigation and recovery.
- Security Awareness and Training Program: This program ensures that employees are educated about cybersecurity best practices and threats. Regular training helps reduce the likelihood of social engineering attacks and other human-related security risks.
- Risk Management Policy: This policy defines how the organization identifies, assesses, and manages cybersecurity risks. It includes risk assessment processes and risk mitigation strategies.
- Network Security Policy: This policy covers the configuration and use of network security tools, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and VPNs. It also addresses remote access and wireless network security.
- Endpoint Security Policy: Defines security measures for endpoint devices (computers, smartphones, etc.), including requirements for antivirus software, endpoint encryption, and the use of personal devices (BYOD).
- Physical Security Policy: Addresses security measures for protecting physical assets, such as servers, datacenters, and sensitive paper documents.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Plan: Ensures that the organization can maintain critical functions in the event of a disaster or cybersecurity incident. It includes data backups, recovery processes, and alternative work arrangements.
According to Cybint Solutions, 95% of cyber breaches are due to human error whether it is from clicking on dangerous links or falling for email scams; cybercriminals and hackers look to infiltrate a company through its weakest link — its employees. Businesses must educate their employees about cybersecurity best practices, and inform them of what they need to look out for to prevent a breach from occurring. For example, oftentimes a malicious link might come through their email and the employee needs to know how to determine if an email is legitimate or not, and when they shouldn’t click or provide their personal information.
Unfortunately, while cybersecurity tools and processes are generally effective, they still may fail from time to time, whether from advanced persistent threats (APT) or exploits of zero-day vulnerabilities. In addition to practicing cybersecurity, organizations must also establish a cyber resilience framework, or plan for what they will do if a breach does occur. For more information about cyber resilience, check out this Beginners Guide.
What Are the Benefits of Cybersecurity?
Data Protection
The largest benefit to implementing cybersecurity technologies and processes, is the protection it provides for your business, its employees, and customers. Cyber threats are on the rise, with an attack occuring every 39 seconds, and one in three Americans affected by a breach each year. Nowadays, a breach can impact an organization in many different ways, from interrupting day-to-day operations, to hindering customer loyalty, to losses in earnings and revenue. Cybersecurity tools are your organization’s first line of defense, and will help keep unauthorized individuals and cyber criminals from accessing your private digital assets and impairing your business productivity.
Reputation Management
One of the biggest and most significant consequences of a data breach, is the impact it has on customer trust and loyalty. According to a study by Frost & Sullivan, when personal data is exfiltrated in a data breach, half (48%) of consumers also view the incident as a breach of their trust and stop using the online service that lost control of their data. Having a strong cybersecurity program in place not only boosts defense and shortens reaction and mitigation time, but as a result also improves the organization’s reputation; it gives customers a greater feeling of comfort and safety, knowing they’re involved with a business that wants to keep their information secure.
Preventing Financial Losses
Cybersecurity helps prevent financial losses due to cyberattacks, fraud, and ransomware attacks. It can also reduce the cost of recovering from security incidents. According to IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million. Undergoing a breach can be incredibly expensive, and have a significant impact on an organization’s revenue (especially for small-to-medium sized businesses).
Compliance with regulations
For many industries there are regulations that require businesses to follow specific compliance laws (i.e. HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR,) when it comes to cybersecurity, and those businesses can be fined heavily if they don’t adhere to those data protection regulations.
In today’s increasingly digital and interconnected world, cybersecurity is essential for protecting against a wide range of online threats and risks. Implementing robust cybersecurity practices and technologies can help organizations enjoy these benefits while reducing the potential negative impacts of cyberattacks and data breaches.
Cybersecurity and Edge Computing
In an edge computing environment, applications, computation, and data storage are all carried out near the source of the data (i.e. at the “network edge”), as opposed to in the cloud or at an offsite datacenter. Several different types of environments benefit from implementing edge computing solutions, including remote and branch offices, retail stores, industrial IoT, and manufacturing sites. You can learn more about edge computing in this Beginners Guide.
While there are many benefits to implementing edge computing infrastructure, it also raises concerns about cybersecurity, as it creates more systems or devices to secure, and more avenues for threats to enter through. IT teams often consider edge computing as more of a threat than an opportunity, mainly because of this dramatically increased endpoint attack surface.
Oftentimes, organizations with edge servers and edge-based devices and applications rush to implement these solutions, and forego security considerations. However, it is incredibly important that edge environments implement proper cybersecurity tools and processes to ensure their data isn’t compromised. Organizations utilising edge computing must be mindful when it comes to protecting the data they create, and adopt a holistic approach to cybersecurity that covers their entire network and all of their endpoints.
StorMagic and Cybersecurity
There are a number of different cybersecurity tools that can be used to defend an organization from a breach, but one of the most effective is encryption. Encryption solutions ensure that sensitive information is kept private and give businesses peace of mind, knowing that the confidentiality of data is well protected. StorMagic SvSAN features data-at-rest encryption that is FIPS 140-2 compliant and eliminates the need for complex, expensive specialist hardware, and OS or hypervisor-level solutions.
Key management systems (KMS) secure organizations’ encryption keys, to prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing and corrupting sensitive data that has been protected through encryption. StorMagic SvKMS is a powerful key management solution that allows organizations to store keys anywhere — whether it be at the edge, in the datacenter, or cloud. It adapts to and integrates with any environment, to deliver flexible, robust, simple key management, all within a single platform, at a surprisingly low cost.
To learn more about StorMagic SvKMS, visit the product overview page or download our SvKMS data sheet.


